ATCOR Advances Medicine Through Improved Patient Outcomes
For 30 years, ATCOR has been the gold standard in personalized and comprehensive vascular health solutions, improving patient outcomes for clinical trials, academic clinical research, and patient healthcare.
Explore how ATCOR’s digital vascular biomarker monitoring benefits patients everywhere.
Targeted Therapeutic Patient Monitoring
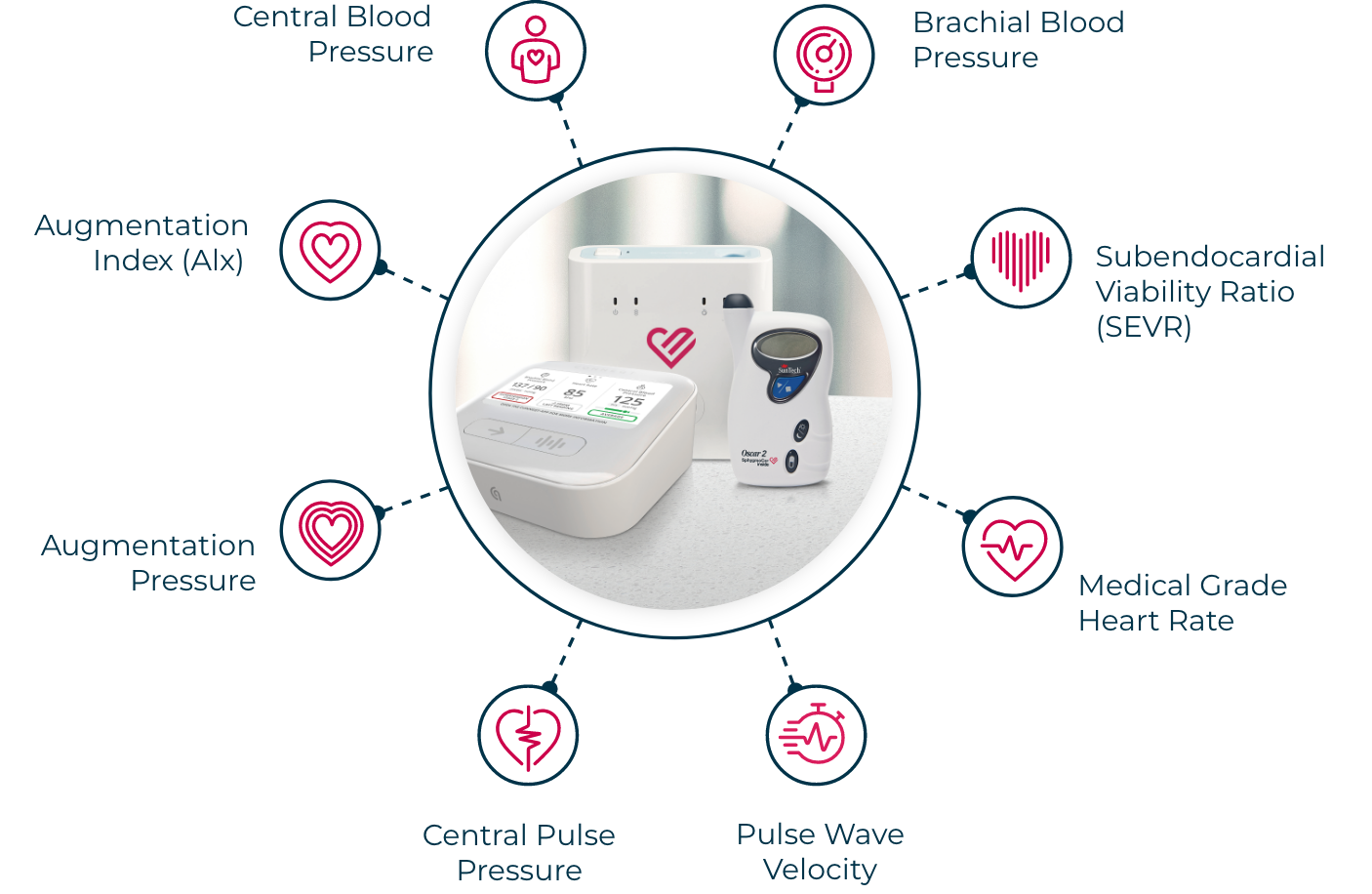
Expand vital signs monitoring with ATCOR’s digital vascular biomarkers. Vascular health risk factors impact chronic disease. ATCOR’s mission is to identify these relationships to advance medicine and improve patient outcomes.
Novel ATCOR digital vascular biomarkers monitor the world’s largest health disorders
Powered by SphygmoCor®
Gold Standard in
Digital Vascular
Biomarkers
8 out of the top ten Pharma companies have used SpyhgmoCor technology in their clinical trials
>1400 papers have been published in leading peer-reviewed journals
All of US News & World Reports’ Top 20 hospitals use SphygmoCor technology to measure digital vascular biomarkers