Understanding Digital Vascular Biomarkers: What Is Pulse Pressure?


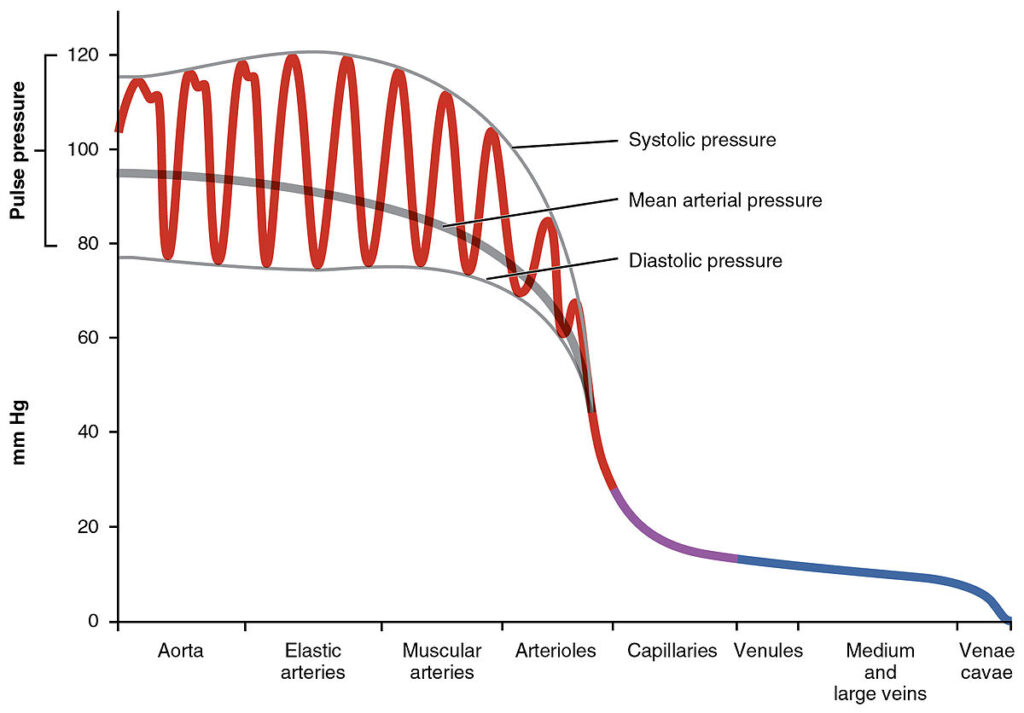
The maximum pressure of the heart when beating is known as systolic pressure. Between heartbeats, when the heart relaxes, the pressure is known as diastole. Pulse pressure represents the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The higher the central pulse pressure, the greater the pressure exerted on organs such as the heart, brain and kidneys. In addition to increasing the risk of heart and circulatory problems, studies show elevated central aortic pulse pressure can independently predict end organ damage like renal failure and Alzheimer’s.
What Is a Normal Pulse Pressure?
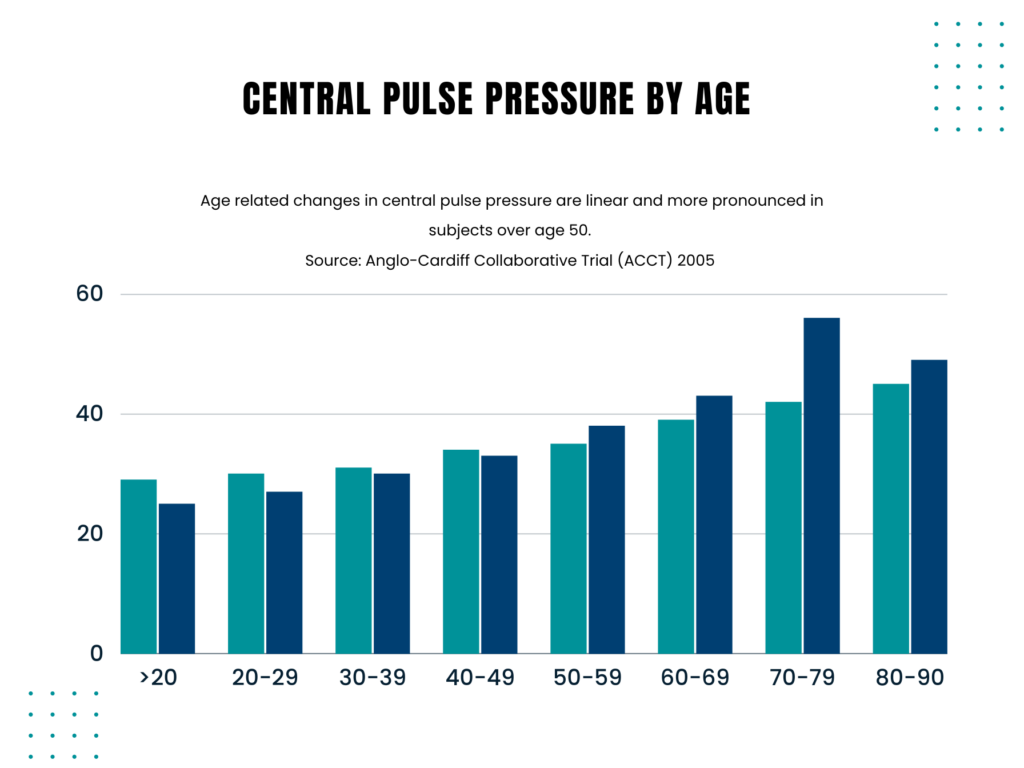
If your resting blood pressure is 120/80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), your pulse pressure is 40. This is considered a normal, healthy pulse pressure. Any pulse pressure reading over 40 mm Hg should be monitored as it could be an early warning sign of an increased risk of heart attack, stroke or other circulatory problems. Studies show an increase in pulse pressure as minor as 10 mm Hg can elevate the risk of heart disease by 20 percent.
As people age, their arteries naturally stiffen. The process of arterial stiffening can be accelerated by negative lifestyle factors such as a poor diet, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle. The stiffer the arteries, the faster blood moves through the circulatory system. As a strong pulse wave of blood moves from the aorta to the narrow capillaries, it hits a wall and some of this blood gets reflected back to the heart prematurely while the organ is still trying to push out out blood (systole). This increased pressure puts an enormous strain on the heart.
How is Central Pulse Pressure Measured?
SyphygmoCor Excel combines a traditional brachial blood pressure cuff with wave form analysis to non-invasively measure pulse pressure and other biomarkers associated with arterial stiffening, including central blood pressure and augmentation pressure. Using this technology, researchers and clinicians can monitor patients for changes in their pulse pressure, along with other clinically relevant digital vascular biomarkers including central and peripheral systolic blood pressure, central pulse pressure, augmentation pressure, true heart rate and SEVR (subendocardial viability ratio, an indicator of how well the heart can meet the demands placed on it). Together these measurements provide a comprehensive and nuanced picture of arterial health, improving patient outcomes and optimizing the safety and efficiency of clinical trials. Embraced by all 20 of the best hospitals in the country and 8 out of ten leading pharmaceutical companies, this “gold standard” technology has appeared in over 4,000 studies published in leading peer-reviewed journals.



